NEW IN CONTINUUM 2021, the BCC+ Rack Focus filter replicates a true camera defocus by introducing lens Bokeh effects. Bokeh is the Japanese term that describes the quality of out-of-focus points of light. In defocused areas, each point of light becomes a shape–either a circle or a polygon. The shape grows in size as the amount of defocusing is increased.

Presets and the FX Editor
To select from a selection of factory installed and user-generated presets, open the FX Editor interface and pick one from the Presets window.
Filter Parameters
Blur: The image is blurred by using a quality blur.
Aperture
Blend: Determines the blend mode to be used when adding Bokeh.
- Add: Bokeh’s are added to your image.
- Screen: The Bokeh are combined with the image using a Screen blend mode. This looks kind of like the Add blend mode, but highlights are retained.
Brightness: Brightens the Bokeh.
Facets: Set the number of Bokeh facets when the Curvature parameter is set to 0.
Curvature: Controls the curvature of the Bokeh. When set to 100, the Bokeh are completely round. Set to a value of 0 to see a polygonal shape.
Angle: Rotates the Bokeh.
Color: Sets the Bokeh color.
Blur: Sets the softness of the Bokeh. This can be useful when using high threshold values.
Matte
A matte is used to create the Bokeh effect.
Position: Pinpoints the color values to be used in the matte. For a luminance matte, a Position value of 100 would make a white matte of the highlights and a value of 0 would make a white matte of the shadows. In the flower image below, look at how the matte varies for different Position values in a red extraction. When the Position is at a value of 100, the red flowers are shown as white in the matte.

When the Position is moved to 50, the red flowers turn black.
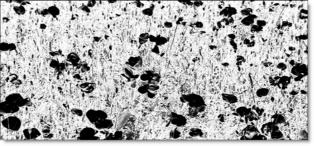
Range: Increases or decreases the range of values in the matte. A low Range value indicates a narrow range of values. A high Range value indicates a large range of values included in the matte.
PixelChooser: The BCC PixelChooser provides simple, built-in masking of the effect result. The PixelChooser is generally used to select a portion of the image and restrict an effect to just the selected area while maintaining the original image content in unselected regions. The selection can be based on geometric shapes or on the image’s luma/color properties.
For more information on the PixelChooser, Click Here.
Working with The Filter
- Apply BCC+ Rack Focus from the BCC Optical Diffusion unit.
- Click the BCC FX Editor button. The FX Editor user interface opens and consists of Presets, Parameters and Viewer windows.
- Try out some of the presets.
- Adjust the Blur to your liking.
- Set the Aperture > Brightness and Color settings.
- Change the Aperture > Facets to control the polygon’s shape and use Angle to rotate the Bokeh.
- Set the Aperture > Curvature to 100 if you prefer the Bokeh to be circular in shape.In some of the filters, a matte is generated to create the desired effect–in this case, Bokeh effects.
- Set your View to Matte to see the matte values.The matte has been preset to a highlight matte to generate the Bokeh effect. The areas that are white in the matte are the areas where Bokeh will be introduced. The location of the Bokeh within the scene can be adjusted by modifying the Matte > Position and Range controls.
- Change the Matte > Position parameter if you want to select different luminance values to be used for the matte.Bokeh will be generated wherever there are white values in the matte.
- Change your View to Aperture to see the Bokeh.
- Increase the Matte > Range value to add more Bokeh into the scene. Decrease for less Bokeh.
- Change your View to Output to see the filtered image.
- Click the Apply button to return to the host application.
The values of the parameter adjustments in the FX Editor user interface are transferred to your host application.