Overview
The BCC Extruded EPS filter enables you to import extrude and animate 2D vector artwork using either the native Adobe Illustrator .ai or .eps format. Retain the original colors in the imported eps/ai file or create your own using the built-in material shader controls. Users of After Effects, HitFilm, and Nuke can take advantage of tight integration with the native host 3D camera and lighting systems in addition to the filter’s own built-in 3D camera and lighting options that are available across all hosts. Additionally, AE users can use AE native mask tools to create custom bevel shapes and for non-AE users, a variety of built-in bevel shapes have been included. Also included with this filter are 3D deformers, such as ripple, pulse, bend-taper-twist, curl and a shatter explosion effect.
As with all filters in the 3D Objects group, this OpenGL based filter is hardware assisted for enhanced render performance.
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Applying the BCC Extruded EPS Filter
3D Objects filters are general best applied to solid color/slug layers which match the dimensions of the overall project. It is recommended that you apply the filter to a project/comp sized layer when possible to ensure that features such as host native Camera and Light integration will work as expected.
Although the Extruded EPS filter operates in a true 3D space, for best integration of the 3D extrusion into an host 3D scene it is generally recommended to leave the Solid layer the filter is applied to as a 2D layer (rather than switching it to a 3D layer).
Use the External File selector to load an EPS file.
 |
 |
Use the Watch Folder to help the filter finding missing external image files such as might happen when moving projects from one machine to another.
 Extruded EPS supports Illustrator 8 EPS and ai files. Please note that we do not currently support Pantone color library. All EPS files must be RGB, not CMYK. Extruded EPS supports Illustrator 8 EPS and ai files. Please note that we do not currently support Pantone color library. All EPS files must be RGB, not CMYK. |
 |
 |
Global Preferences [BCC9 only]
[This preference applies only to BCC9 and is not relevant in newer versions of BCC.] The 3D Objects family of effects relies on the BCC Preferences panel to optimize your configuration based on your workflow needs and the capabilities of your graphics hardware. In particular if you wish to work with footage resolutions higher than 1920×1080 (up to 4k) or to optimize antialiasing settings for your hardware, please consult the documentation on Managing BCC Preferences.
Built in Filter Presets
There are several levels of built-in preset controls in the Extruded EPS filter ;
There is a master preset control for saving and loading values for all the parameters in the filter. This is the 1st preset control, near the top of the Effect Controls panel.
There is a Saved Path preset control for saving and loading custom curves based on AE masks (to act as the fundamental path which is being extruded by the filter).
There is an Extrusion Style preset control for saving and loading a style that includes all the Extrusion and Material attributes.
There are 3 preset controls (Bevel, Side, and Path) for saving and loading custom curves created out of AE masks (for use in defining extrusion shapes and the path to be extruded).
There are Material preset controls for saving and applying materials used on the extrusion surfaces.
 |
Render
The Render parameter group includes controls that can affect the smoothness and edge quality as well as some other options that affect the visual quality of the Extruded EPS effect.
The Polygon Count parameter can be used to increase or decrease the number of polygons defining the extruded object. If curved edges or surfaces of the extrusion look blocky, increasing the Polygon Count will result in the curves looking smoother. The performance of the filter is affected by the Polygon Count and it is possible to speed up the performance (during preview or exporting the final effect) by reducing the Polygon Count.
The Antialiasing popup menu controls the level of antialiasing applied to the edges of the Extruded EPS. If the edges of the Extruded Spline look jagged, increasing the Antialiasing level can help smooth the appearance of the edges. The performance of the filter is affected by how much antialiasing is being applied and it is possible to speed up the performance (during preview or exporting the final effect) by reducing the Antialiasing level. Be aware that when the AE layer the filter is applied to is set to Draft in the AE timeline the Antialiasing popup menu has no effect and the Extruded EPS uses Draft antialiasing regardless of how the popup menu is set. Likewise in Avid hosts if the Follow Avid Draft Setting checkbox is enabled, the filter will render in draft mode when Avid is at less than full resolution (i.e. either yellow/yellow or yellow/green) and you will only see the antialiasing results when Avid is set to full green/green resolution. Note that important additional hardware based antialiasing options are also available in the BCC Preferences panel.
The Transparent Object checkbox can allow for a more realistic appearance when using partially transparent (as opposed to fully transparent or fully opaque) materials on extruded surfaces.
The Motion Blur parameters offer control for simulating a camera blur for motion resulting from animation of the Extruded EPS. Enabling Motion Blur will noticeably slow down the preview and render time for the effect, so it is recommended to enable it as a last step when designing the effect. Also, notice that the Enable Motion Blur checkbox parameter is keyframable so it is possible to only enable it for the frames within the effect including significant motion – thereby speeding up preview of some areas and speeding up the overall final render of the effect.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Using Host 3D Camera and Lights
Some hosts support direct integration with the host’s native 3D Camera (AE, Nuke, HitFilm) and 3D lights (AE and HitFilm).
By default the 3D object is lit by a single built-in point light centered and positioned in front of the extrusion and by any host lights enabled in the comp if Use Comp Lights is enabled and it is a supported host.
If both the Use Comp Lights and the Use Built-in Light checkboxes are enabled it can be lit by both the BCC built-in light and the host native comp lights.
When using AE lights, the 3D object will properly support all host light types (Point, Spot, Ambient, or Parallel)
There is information specific to using the Built-In Light controls later in this document.
If an active host camera is present in the comp, the 3D object can be viewed from the perspective of the hosts 3D camera by enabling the Use Comp Camera checkbox in supported hosts.
If there is more than one camera track spanning the current frame, and the host comp window set to “Active Camera” the 3D object will use the perspective of the camera whose track is nearest the top of the timeline. If there are multiple cameras and the hostcomp window is set to use a specific camera (other than the topmost camera) the 3D object will use the camera specified by the comp window. In this sense the filter simply follows the behavior of 3D layers (e.g. in AE).
There is information specific to using the Built-In Camera controls later in this document.
 |
Extrusion
The Extrusion parameter group includes controls for adjusting the shape (geometry) of the Extruded EPS object.
The Extrusion Depth parameter defines the depth of the side face that extends between the front and back of the Extruded EPS.
The Bevel Style popup menu offers choices for Straight, Convex, Concave, Saved Preset, or Host Path. The Host Path choice allows for creating a custom bevel based on an AE mask, and the Saved Preset choice allows for using a preset created by saving a bevel style based on an AE mask.
The Bevel Amount parameter determines the depth of the edge bevels for the Extruded EPS.
The Back Bevels checkbox enables edge bevels between the side and back face of the Extruded EPS.
The Side Style popup menu offers choices of Straight, Saved Preset, or Host Path. The Host Path choice allows for creating a custom side face based on an AE mask, and the Saved Preset choice allows for using a preset created by saving a side style based on an AE mask.
The Bevel Host Path and Side Host Path popup menus are where it is possible to select an AE mask as a custom extrusion curve (if Bevel Style or Side Style is set to Host Path, other wise these controls are disabled).
The Bevel Saved Preset and the Side Saved Preset controls are where you can access bevel or side preset styles that have been saved based on AE Masks. To save such a bevel or side style preset the Bevel Style or Side Style popup menu must be set to Host Path and an AE mask must be selected as the Host Path. Once the preset is saved, it will work even in effects that do not include that particular AE Mask.
Note that for an AE Mask to be accessible to the filter it must be applied to the same AE layer the filter is applied to, and for the mask to have the expected effect as a custom bevel or side curve it must be an open path. The images below show various AE mask curves applied to the side face of an Extruded Spline
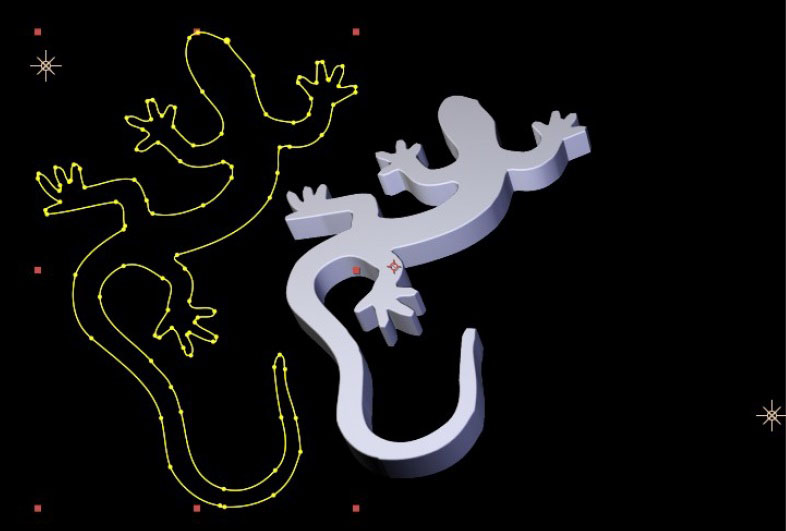 |
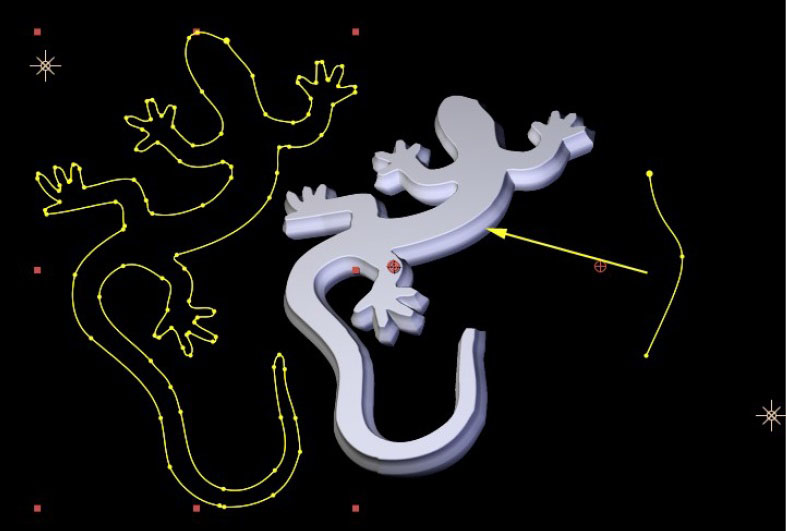 |
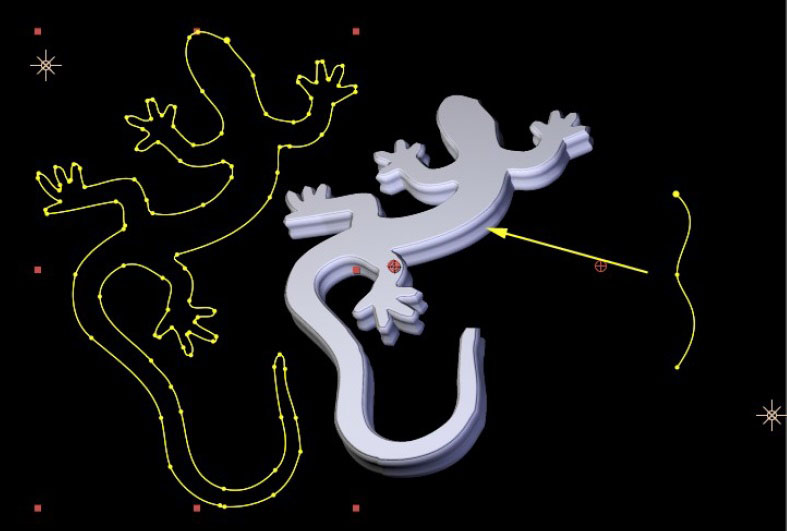 |
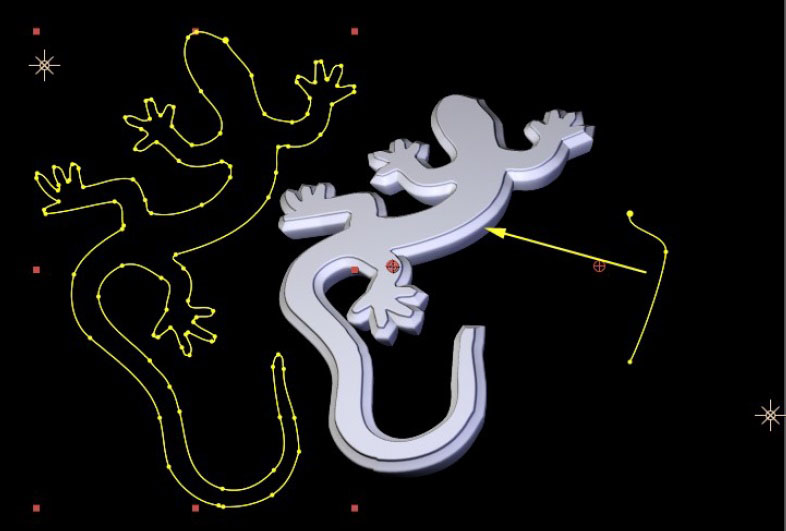 |
Material
Material parameters are used to determine the appearance of the surface(s) of the Extruded EPS.
The Ambient Intensity parameter controls the ambient light amount on all materials for an extruded object, unless there is an active AE Ambient Light track in the comp, in which case the ambient light is controlled there and Ambient Intensity will have no effect.
The Keep EPS Color checkbox allows for the EPS file’s original color to be used.
The Material Count popup menu determines which faces of the extrusion share materials and which of the 4 Material parameter groups are used (and have their controls enabled) is determined by this popup menu.
The Material Preset control is where it is possible to save or apply preset materials. Material Presets include all parameters of a material except Texture Layer or Bump Layer (because these parameters refer to other layers in the AE comp and so are not available in all contexts the style may be used). To save a material preset style including texture or bumps, use a texture or bump map from the Texture File or Bump File popup menu since these files are accessed directly from disk as a resource of the plugin so that they will be available in whatever context the style is applied.
The Front Texture File popup menu allows for selecting a texture to map to the surface of the 3D object. Texture maps accessed through this menu can be saved as part of preset styles (Material presets, Extrusion presets, Filter master presets). The texture maps pre-installed in this menu are graphics designed to simulate materials like stone, tiles, metal, and wood – and they are designed to seamlessly tile so that when they are used the surface should look continuous at any scale, rotation, or position offset. The pre- installed texture files are from the Genetica Texture Packs created by Spiral Graphics [http://www.spiralgraphics.biz/] It’s possible to add more textures to this menu by placing them in the correct directory on your hard drive. The directories for the Texture Files menu graphics are as follows ; On Mac OS [Macintosh HD\Library\Application Support\BorisFX\BCC 6.0\Styles\Custom Textures] and on Windows [C:Program Files\Boris FX, Inc\BCC Presets 6\Custom Textures]. The Texture File feature supports several still graphic formats such as ; psd, bmp, png, tif, tga, pct, jpg, gif.
The Texture Layer popup menu is where it is possible to select an alternate layer within the AE comp to use as a texture mapped to the surface of the 3D object. This allows for using any AE supported media files (including moving video) as a texture map.
The Texture Alpha popup menu allows for specifying how to interpret (or even disable) the alpha channel on a texture map.
The Texture Strength parameter allows for fading a texture map which reveals some of the diffuse color underneath. At a value
of 1 the texture map is fully opaque and it fades as the value is lowered.
The Ambient, Diffuse, and Highlight color parameters determine the colors for the material.
The Opacity parameter controls the opacity of the material. When using partially transparent materials, enabling the Transparent Object checkbox in the Render group may create a more realistic looking effect.
The Highlight Amount parameter controls how much of a highlight will be reflected on the surface of the object. There is more of a highlight at lower values and less at higher values. A visible highlight is also dependent on the Highlight color chip being adjusted to a color with some obvious luminance.
The Specular Strength parameter controls how intense (shiny) the highlight is.
The Front Bump File popup menu allows for selecting a bump map for the surface of the 3D object. Bump maps accessed through this menu can be saved as part of preset styles (Material presets, Extrusion presets, Filter master presets). The menu accesses graphics from the same directory as the Texture File popup menu.
The Front Bump Layer popup menu is where it is possible to select an alternate layer within the AE comp to use as a bump map on the surface of the 3D object. This allows for using any AE supported media files (including moving video) as a bump map.
The Bump Strength parameter controls the intensity of the bumps generated by the bump map.
The Shift X and Y, Scale X and Y, and Rotate parameters allow for offsetting the position, scaling, and rotating the texture and bump maps.
The Reflection popup allows for selecting a reflection map for simulating a reflection on the surface of the 3D object. The directories for the Reflection menu graphics are as follows ; On Mac OS [Macintosh HD\Library\Application Support\BorisFX\BCC 6.0\Shaders\Images] and on Windows [C:Program Files\Boris FX, Inc\Lib\BCC6.0\Shaders\Images]. Reflection maps must be DDS file cube maps, which is a special 6 sided graphic which allows for a reflection that simulates a true fully surrounding environment.
The Reflectivity parameter controls how much of the reflection map is mixed in to the look of the material.
The Reflection Scale parameter scales the appearance of the reflection map.
The Two-sided Lighting checkbox causes a material to display the effects of lights on both sides when the checkbox is enabled. This can be useful for achieving specific types of effects.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Transformations
The Transformations parameter group includes controls for Rotating, Positioning, and Scaling the 3D object
The Orientation X, Orientation Y, and Orientation Z parameters offer an initial set of rotation controls for orienting the 3D object. Used in conjunction with the Rotate X, Y, and Z controls it is possible to create animations that would not be possible with a single set of rotation controls.
The Rotate X, Rotate Y, and Rotate Z parameters offer rotation controls for the 3 3D axes, and the order in which they are applied to the object matches the X, Y, and Z Rotation of AE 3D layers making it easy to match the rotations from such AE layers and even to link the rotation parameters of the 3D object to other layers using AE expressions
The Position X, Y, and Z parameters offer world based position controls for the Extrusion
The PreRotate Position X, Y, and Z parameters offer object based position controls for the Extrusion
The Master Scale parameter increases or decreases the X, Y, and Z scale of the Extrusion
The individual Scale X, Y, and Z parameters offer individual control of Scale along each axis. It’s possible to offset the individual scale values to change the scale ratio and then to globally scale the result while maintaining that ratio by using the Master Scale parameter. Be aware that the Scale Z parameter is not the commonly desired way to increase the depth of the extrusion – there is another parameter offered in the Extrusion group which scales only the extrusion face (not bevels etc.) which is more commonly used for this purpose.
The Opacity control in the Transformations group controls the opacity of all materials for the 3D object. When using partially transparent materials, enabling the Transparent Object checkbox in the Render group may create a more realistic looking effect. Keep in mind that this is a different effect from fading the opacity for the AE layer the filter is applied to which is the recommended way of uniformly fading the filter effect.
Pivot X, Y, and Z allow for offsetting the pivot point around which the 3D object rotates, unless Lock Pivot to Position is enabled in which case these controls are disabled and the Pivot point follows the position point.
Built-in Light (1-3)
The Built-in Light parameter groups include controls for light sourcea that can be controlled from within the filter. Additional lights can be added by creating host light tracks in hosts that support full integration with their native 3D lighting systems such as AE and HitFilm. The Built-in Light offers 3 Light Types to choose from: Point, Spot, and Spot + Shadows
Point: A Point light shines from the source in all directions and includes controls for X/Y and Z Position, Color, Intensity, and Attenuation. Attenuation lessens the intensity of the light rays as they extend from the source, allowing for the creation of a less directional distant diffuse light, similar to sunlight.
Spot: A Spot light shines from the source toward a target (specified by Spot X/Y and Z parameters) and is limited to a cone defined by the Angle parameter and with edges softened by the Fall Off parameter.
Spot + Shadows: A Spot + Shadows light is identical to a Spot Light, except that it is also capable of casting shadows. The shadows it casts are limited to self-shadowing between 3D objects generated by the filter. The Width parameter can appear to soften the cast shadow edges. The cast shadows do not support partial transparency – meaning the shadows will appear as if the object being shadowed is fully opaque or fully transparent – and the Alpha Shadow Tolerance parameter defines the threshold for what the shadow considers opaque or transparent.
Built-in Camera
The Built-in Camera parameter group includes parameters that affect the viewing perspective of the 3D object whenever the Use Comp Camera checkbox is not enabled. When using the Built-in Camera, there are 3 options for what kind of Camera Model is used: Position, Orbit, or Pan.
Zoom: all 3 Camera Models include a Zoom control for zooming the viewing perspective. By using a low Zoom value, and moving closer to the 3D object with the Position Z parameter (or Orbit Radius or Pan Distance depending on the Camera Model), it’s possible to simulate a more wide angle lens perspective.
Position Camera: offers Position X, Y, and Z control for positioning the camera in 3D space, and offers 2 Camera Orientation
options: Free or Target.
- When using Free Camera Orientation, the direction the camera is pointing is determined by the Tumble, Spin, and
Rotate parameters. - When using Target Camera Orientation, the camera will always point in the direction of the target as determined by the
Target X, Y, and Z parameters.
Orbit Camera: provides a convenient camera perspective for always facing the center (default Position of the 3D object) while allowing for simple orbit moves around the center using the Orbit Tumble, Orbit Spin, and Orbit Rotate parameters. Distance from the Center is determined by the Orbit Radius parameter.
Pan Camera: offers simple controls for panning horizontally using the Pan Advance parameter, and moving the camera in or out with the Pan Distance parameter.
 |
 |
Deformers
The Extruded Text filter includes several true 3D deformers for warping the 3D extrusion in various ways. The Deformers included in the filter are Bend-Taper-Twist, Curl, Shatter, Ripple, and Pulse.
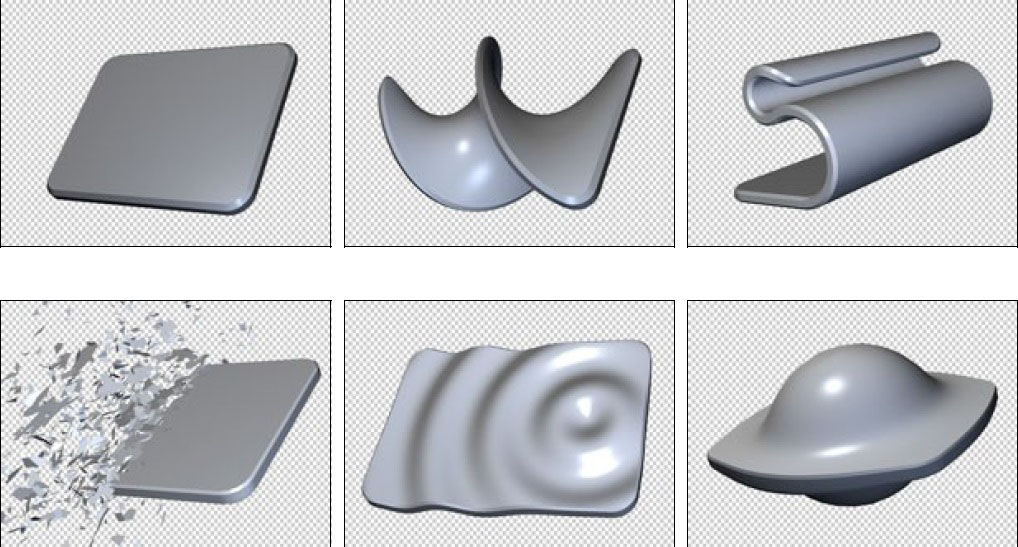 |
Bend-Taper-Twist Deformer
Effect Order
As the name suggests Bend Taper Twist offers 3 distinct deformation processes and the Effect Order popup menu provides a way
to determine the internal order in which the 3 deformations are applied to arrive at the final result.
Bend Strength, Bend Radius, and Bend Mode
Bend Strength controls how much bend is applied and in which direction the bend goes, with positive values bending the left and right edges of the object forward and negative values bending them backward. Bend Radius defines the steepness of the bend curve. The Bend Mode popup menu provides 2 options for how the bend will appear. Using the Stretch mode, the Z scale of the object increases as the Bend radius increases, while the using the Curve mode the Z scale does not change with the Bend Radius.
Left Taper and Right Taper
The Left and Right Taper controls taper the Y and Z scale of each side of the object, with positive values giving a larger Y and Z scale and negative values giving a smaller Y and Z scale.
Left Twist and Right Twist
The Left and Right Twist parameters twist each side of the object, with positive values twisting the object so the top part is bent forward while the bottom part is bent back – and negative values twisting the object so the top part is bent back while the bottom part is bent forward.
Center Offset X, Center Offset Y, and Center Offset Z
Center Offset X, Y, and Z provide a way to offset the deformations in 3D space.
Curl Deformer
Direction
The Direction popup menu determines what direction in 3D space the object will curl in using the Curl deformer. The Guess choice tries to give a commonly desired result by curling along the longest axis in the direction of the shortest axis, and the Guess 2 choice curls along the longest axis in the direction of the second shortest axis. The other choices are labeled to allow for specifying what edges of the object are curled along which 3D axis.
Reverse Direction
The Reverse Direction checkbox reverses the direction of the curl in terms of which edge (Left, Right, Top, Bottom) begins the curl. For example a Left/Right curl begins on the right edge and moves left by default but it begins on the left edge and moves right with the Reverse Direction checkbox enabled.
Curl 1 and Curl 2
The Curl 1 and 2 parameters define a primary and a secondary curl when changed from their default values of zero, with positive values curling the edge of the object forward and negative values curling the edge back in 3D space.
Tightness
The Tightness parameter tightens or loosens the Curl(s) by increasing or decreasing the size of cylindrical area(s) the object is rolled into as it is curling. A higher Tightness value rolls the object into a smaller cylinder while larger values roll it into a larger cylinder, with more or less of the object rolled farther into the cylinder depending on its size.
Midpoint
The Midpoint parameter will only seem to have an effect if Curl 2 is changed from its default to create a secondary curl. In this case Midpoint determines the positioning of Curl 2 in relation to Curl 1
Amount
The Amount parameter offers a way to control the overall progression if the curl effect in a single parameter. This allows for easy creation of animated curl effects where an object rolls or unrolls over time. The Amount parameter defaults to a value of 70 (rather than zero) so that the preceding parameters can be adjusted to design the curl while the effect is visible. For many commonly desired effects the Amount parameter will be animated over time in the final effect. For example in order to have an object begin as curled and to unroll to its un-curled state over time the Amount parameter is animated from some higher number back to zero. And in order to have an object begin un-curled and roll up over time the Amount parameter is animated from zero to some higher number.
Axis Offset
The Axis Offset parameter allows for scaling the curl cylinder larger or smaller without rolling more or less of the object further into the cylinder – instead it will cause the curled part of the object to scale and distort to the new size.
Bend 1 and Bend 2
The Bend 1 and 2 controls provide a way to to bend the object at the point of Curl 1 and Curl 2. The bend(s) are applied along the alternate access from the curl.
Resolution
The Resolution parameter controls how many curl points the deformer uses to internally calculate the curl. In most cases there is no reason to change this parameter from its default, but in some cases it is possible to make the curl appear smoother by increasing the Resolution value.
Curl Type
The Curl Type popup menu offers 2 choices: 3D or Flat. The default choice of 3D will curl the object while maintaining its thickness while the Flat choice will flatten the object at the curl points.
Noise Reduction
The Noise Reduction checkbox, which is enabled by default, prevents noise artifacts that can appear in certain types of curl effects. The speed of the curl effect can be increased by disabling Noise Reduction for effects where it does not seem to be necessary.
Shatter Deformer
Polygon Count
While it is not a parameter within the deformer itself (Polygon Count is a parameter in the Render group), the Shatter deformer shatters 3D objects based on the polygons / vertices that make up the geometry mesh of the shape, so the Polygon Count value (tesselation) of the object has a significant effect on the appearance of the shatter effect. Higher Polygon Count values result in more overall shatter pieces that are smaller, and lower Polygon Count values result in less overall pieces that are bigger. Lower Polygon Count values also result in faster performance. There are also ways to affect the size and number of the pieces from within the Shatter deformer itself.
Crack Mode, Crackability, and Crack Adjust
The Crackability parameter determines the size of the pieces with higher values resulting in smaller pieces and lower values resulting in larger pieces. Also, very low Crackability values can result in some parts of the object not being affected by the shatter (not being Crackable) at all. The Crack Adjust parameter affects the shatter in different ways depending on which Crack Mode is being used (explained in more detail in the bullet points below). The Crack Mode popup menu includes 5 modes. Each Crack Mode has a unique way of influencing how the object will shatter in terms of how many places it cracks and where it cracks while shattering ;
- Random mode creates apparently randomly placed cracks. In this mode, the Crack Adjust parameter has no effect.
- Crack Points mode creates cracks that include cracks in areas of the geometry where various parts are connected. For example in an extruded shape crack points would include the place where the front face meets the bevel, where the bevel meets the depth face, etc.
- Falloff Crack Points mode is similar to Crack Points, but falloff means the Crackability decreases farther from the Crack Points which can be used to create a more realistic shatter effect in some cases.
- Horizontal Lines makes horizontal cuts through the mesh creating alternating horizontal lines of bigger and smaller pieces and the Crack Adjust parameter can be used to increase or decrease the number of lines.
- Angular Cut breaks the mesh at all points where the mesh edges are a certain angle, while Crack Adjust and Crackability determine what angle that is and how close to the angle they have to be in order to break.
 |
Velocity Mode, Velocity Minimum, Velocity Variation, Explosive Force, and Gravity
The Velocity Mode popup menu offers 12 options for determining the direction the shatter pieces will move in relation to the object as it shatters. The Velocity Modes are ;
- Random
- Outward
- Inward
- Spiral CW (Clockwise)
- Spiral CCW (Counter-Clockwise)
- Left-Right
- Left
- Right
- Up
- Down
- Back
- Forward
Velocity Minimum determines the minimum velocity for the slowest of the shatter pieces, while Velocity Variation determines how varied the velocity is between all the pieces, and also acts as a maximum velocity control. Explosive Force provides an easy way to alter the overall velocity curve so there is a burst of speed as the piece first shatters away from the main shape – the Explosive Force also gives a similar speed burst to the Spin Speed of the pieces which makes the explosive feeling of the shatter more convincing. Gravity exerts a pull on the shatter pieces (unless it is set to zero), and although it is outside of the slider range it is possible to scrub the numeric entry field or enter negative Gravity values to apply reverse gravity. To have no velocity to the shatter (so the object seems to crumble) set both Velocity Minimum and Velocity Variation to zero, and make sure there is some
gravity value applied.
Scatter Wipe Mode, Wipe Time, and Scatter Option
It is possible to have the shatter effect progressively wipe from one part of the object to another rather than having the whole object shatter at once. This can be done by choosing one of the Scatter Wipe modes. The Scatter Wipe Mode popup menu offers 12 options for determining the direction the wipe will move in relation to the object. The Scatter Wipe Modes are:
- None (no wipe, object will shatter all at once)
- Left – Right
- Right – Left
- Top – Bottom
- Bottom – Top
- Back – Front
- Front – Back
- Random
- Small – Large (small pieces first, followed by large)
- Large – Small (large pieces first, followed by small)
- Inside – Out
- Outside – In
Wipe Time determines how long the wipe takes from start to finish, with higher values resulting in longer wipes and lower values resulting in shorter wipes. The Scatter Option parameter is relevant when applying a Scatter Wipe to an object that includes multiple parts (like Extruded Text characters) ; in this case, the Scatter Option Smooth choice results in a wipe that moves across all the parts as if they were one large whole, while the Discreet choice results in a wipe that acts as several individual wipes that move simultaneously across each part. The difference between the Smooth and Discreet Scatter Options is illustrated using Extruded Text immediately below.
Displace
The Displace parameter allows for pushing the shatter pieces out away from (or in toward) the center of the object. Positive Values push the pieces outward and negative values pull the pieces inward. This displacement is in addition to whatever shattering is going on based on other deformer parameters.
Keep Threshold
The Keep Threshold parameter allows for making it so some percentage of the shatter pieces stay in place rather than shattering away from the original object. Adjusting this parameter with various combinations of Crack Modes, Crackability, and Crack Adjust can give some interesting results.
Spin Direction, Spin Speed, and Spin Character
The Spin Direction popup menu includes 7 options for determining which direction the shatter pieces will rotate as they shatter from the original object. The Spin Directions are ;
- Random All (all pieces randomly rotating)
- Tumble Forward (all pieces tumbling on the X axis in one direction)
- Tumble Both (some pieces tumbling on the X axis in one direction and some tumbling on the X axis in the opposite direction)
- Spin Forward (all pieces spinning on the Y axis in one direction)
- Spin Both (some pieces spinning on the Y axis in one direction and some spinning on the Y axis in the opposite direction)
- Rotate Forward (all pieces rotating on the Z axis in one direction)
- Rotate Both (some pieces rotating on the Z axis in one direction and some rotating on the Z axis in the opposite direction)
The Spin Speed parameter determines how fast and in which direction the shatter pieces rotate – positive values will cause a piece to rotate in one direction while negative values will result in that piece rotating in the opposite direction, and the rotation will be faster the further away from zero the value is. The Spin Character parameter defines a gradient that maps the difference in spin speed between the largest and smallest shatter pieces, allowing for having the larger pieces spin faster. Since Spin Character relates to Spin Speed, it is suggested to adjust these 2 parameters together in relation to each other.
Time Scale, Time Mode, and Manual Time
By default the shatter effect is set to auto-animate (with Time Mode set to Automated) so no interpolation keyframes are necessary for the object to shatter over time. When the shatter is Automated, Time Scale allows for slowing down or speeding up the overall speed of the shatter. As the parameter name indicates, Time Scale affects the whole time scale of the effect, so it will also affect the timing of a Scatter Wipe (if it is enabled) as well as the Spin Speed of the pieces, and even the effects of Gravity – so it is suggested that these other speed & time related parameters should be adjusted in conjunction with Time Scale. There are 4 Time Mode choices which are ;
- Automated (auto-animation that obeys Time Scale parameter)
- Manual (animation progresses according to the Manual Time parameter and ignores Time Scale parameter)
- Manual Move (the Velocity based movement and Scatter Wipe time progress according to the Manual Time parameter, but the Spin Speed behaves as Automated)
- Manual Spin (the Spin Speed progresses according to the Manual Time parameter, but the Velocity based movement and Scatter Wipe time behave as Automated)
Since the Automated Time Mode always does a forward shatter (Time Scale does not accept negative values), using the Manual Time mode (animating from a higher to lower Manual Time value) is suggested for creating reverse shatter effects.
Random Seed
The Random Seed parameter allows for tweaking the shatter to get a different result without changing any of the other significant parameters that create the look of the effect. This can be useful to help alter the shatter for a particular frame(s) while auto- animating, and it is also very useful for cases where there are multiple objects each using the same Shatter – since an identical appearance can be avoided by simply using different Random Seed values for each instance of the effect. This is a parameter that is left static in most common uses, since animating it will not result in a smoothly animating shatter.
Ripple Deformer
The Ripple Deformer applies a ripple effect along the Z plane of the object.
Center X/Y and Stretch
Center X and Y determine the X/Y center point for the ripple effect. The ripple defaults to being a perfectly round circle ripple and the Stretch parameter allows for elongating the ripple shape in either direction resulting in an oval shape ripple. Combining certain Center X/Y and Stretch values also allows for the creation of effects that can appear more like a wave, including a horizontal or vertical wave.
Phase and Time Scale
The Ripple deformer auto-animates by default and the Phase parameter allows for offsetting the phase of the ripple auto- animation. The Time Scale parameter determines the speed of the ripple auto-animation with negative values animating the ripples outward from the center and positive values animating in the reverse direction, with values farther away from zero being faster and values closer to zero being slower. It is also possible to manually drive the ripple by setting the Time Scale to zero and animating the Phase parameter with keyframes.
Amplitude and Frequency
Amplitude determines the height of the waves and Frequency determines the frequency of waves. Adjusting one of these parameters has some effect on the other so it is recommended to adjust them in relation to each other to get the desired result.
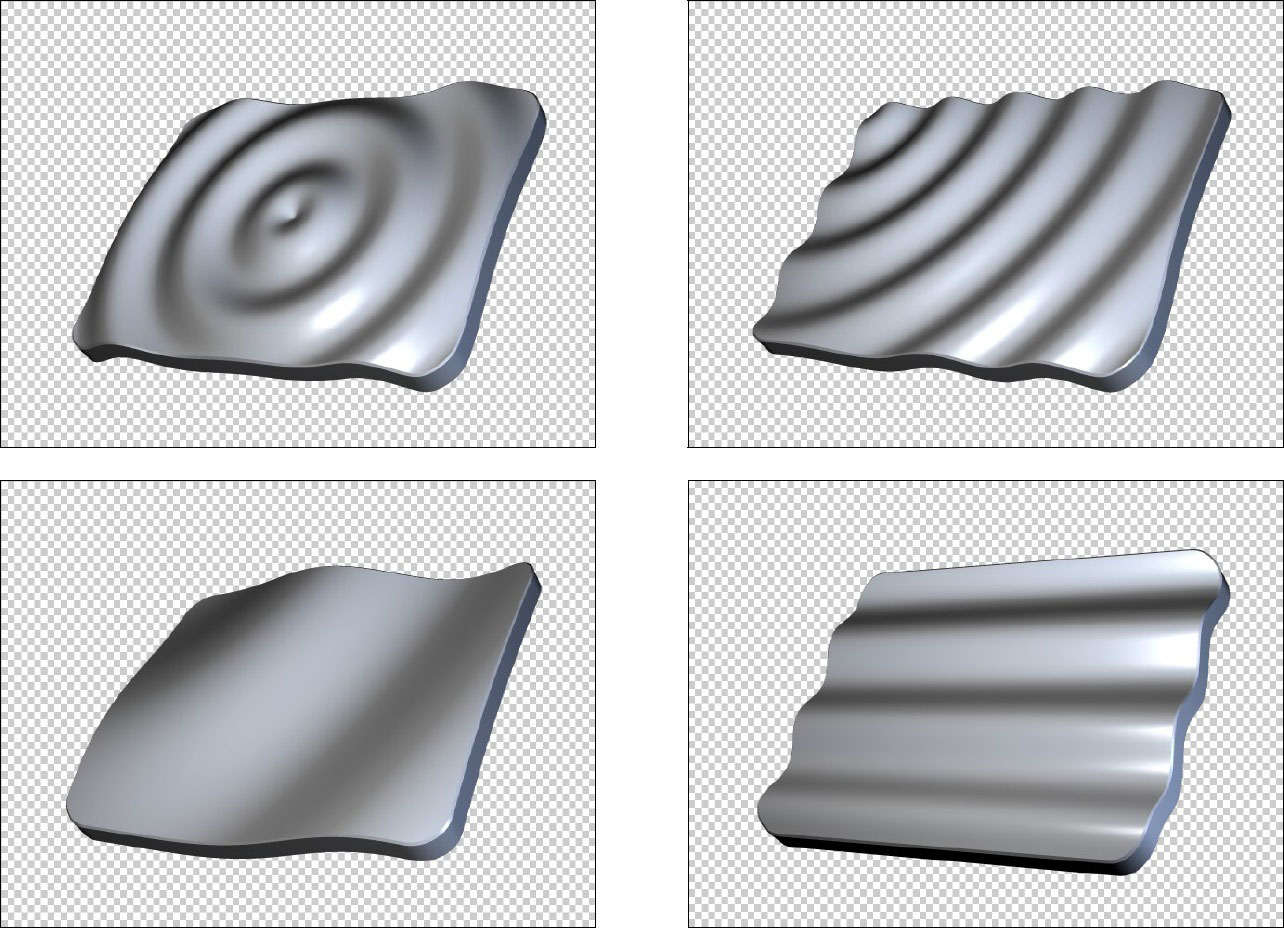 |
Pulse Deformer
The Pulse deformer offers several different deformations (in some cases similar to those found in other deformers) and offers a quick way to apply these deformations using repetitive auto-animation back and forth within a user determined range to allow for convenient creation of pulse like animations without requiring keyframing. The Pulse animation oscillates between the original undeformed object and the deformed object.
Effect Type
The Effect Type popup menu determines which kind of deformation will be applied to the object. There are 8 Effect Type choices ; Bulge, Deform, and Lumpy are variations of a Bulge or sphereize type of effect. Bend, Twist, and Spin do exactly what the parameter names suggest with the Bend and Twist deformations being like those described previously in the Bend-Taper-Twist deformer, and the Spin choice applying a simple spin on the Y axis. Bounce moves the object up and down on the Y axis and Approach moves it back and forth on the Z axis.
Pulse Type
The Pulse Type popup menu determines the animation curve of the pulse cycle as the deformation animates from the original undeformed object to the most deformed state (determined by Amplitude parameter) and back again. There are 9 Pulse Type choices ;
- Breathing creates a pulse where the animation accelerates as it moves away from an extreme and decelerates as it gets closer to an extreme, with a slight pause between each back and forth.
- Elastic pulse is similar to Breathing except with no pause between each back and forth animation.
- Beat pulse decelerates as it moves away from the original undeformed object and uses linear interpolation (even speed) as it animates from the extreme back to the original – with no pause.
- Bop pulse decelerates as it moves away from the original undeformed object and accelerates as it animates from the extreme back to the original – with a pause between pulses.
- Uneven pulse is like elastic but the amplitude of the pulse varies so that some pulses are stronger than others.
- Jerky pulse is like Elastic with a pause added midway between the undeformed and most deformed states, and the interpolation is such that it eases in and out of the extra pause.
- Random pulse will cause the deformation to jump between various values. Using this Pulse Type the Amplitude parameter has no effect (the Random Pulse automatically uses amplitude values between zero and 100). The animation jumps between values using Hold style interpolation – meaning that it snaps between states rather than smoothly animating between them.
- Snap pulse will snap back and forth between the original undeformed object and the most deformed state. The animation jumps between values using Hold style interpolation – meaning that it snaps between states rather than smoothly animating between them.
- Paused pulse disables the pulsing auto-animation and the Frequency and Phase parameters have no effect using this Pulse Type. The other parameters such as Amplitude can still be used to adjust the static effect.
Amplitude, Frequency, and Phase
The Amplitude parameter determines how much of the deformation is applied at the most deformed point in the pulse animation. Although it is outside of the slider range it is possible to scrub the numeric entry field or enter negative Amplitude values to reverse the direction of the deformation. The Frequency parameter determines the frequency of pulses, with higher values resulting in more frequent pulses and lower values resulting in less frequent pulses. The Phase parameter allows for offsetting the phase of the auto-animated pulse. It is also possible to manually drive the pulse (and animate its frequency) by setting the Frequency parameter to zero and animating the Phase parameter with keyframes.
Center Offset X and Y, Radius Adjust
The Center Offset X and Y parameters allow for offsetting the center of the deformation in X and Y space, while Radius Adjust determines the the size of the area in which the deformation is applied. When using the Spin Effect Type, Radius Adjust has no effect.

